Beer's Lambert Law Equation
When working in concentration units of molarity the Beer-Lambert law is written as. Beer-lambert law describes the link between the attenuation of light.

Beer Lambert Law Labster Theory
Beer lambert Law 1.

. Enter the value of the molar absorption coefficient ie 8400 M-1 cm-1. Beers Law A E C l I I T OR log T log A I0 I0 From the equation it is seen that the absorbance which is also called as optical density OD of a solution in a container of fixed path. Type the concentration of the solution ie 433 µmolL-1.
Beers Law is also known as the Beer-Lambert Law the Lambert-Beer Law and the BeerLambertBouguer LawThe reason there are so many names is because more than one law is involved. Beers Law and Lamberts law. 303 coefficient A E C l Beers Law 25.
Beers law also called Lambert-Beer law or Beer-Lambert law in spectroscopy a relation concerning the absorption of radiant energy by an absorbing medium. We can then divide E a by this number which gives us a dimensionless number representing the number of collisions that occur with. Beers Law relates to two variables input intensity I 0 and output intensity I.
303 log K C l I I0 K log C l I 2. According to Beer-Lambert Law. Beers Law I0 2.
Where A Absorption. Well well start with the R TBy multiplying these two values together we get the energy of the molecules in a system in J mol-1 at temperature T. Later in 1760 Johann Heinrich Lambert quoted Bougers discovery saying that the absorbance of a sample is directly proportional to.
Understand the Beer-Lambert law for absorbance A ɛ x l x c. Above equation shows us that the SNR of an X-ray imaging system of. The colorimeter was invented in the year 1870 by Louis J Duboscq.
While studying this topic you will learn about Beers law Lamberts law Beer Lamberts law its derivation graphs related to this law applications of Beer Lamberts law the. Beers Law Example Calculation. And 24 show in addition that the Beer-Lambert law is designed for monochromatic light and its absorption increases with decrease in radiation wavelength.
Equation 6 is the required Beer Lambert Law Formula. For example in molecular absorption spectroscopy we expect the instrument response to follow the Beer-Lambert equation. The colorimeter is usually used to measure the concentration of a known solute in a given solution with the help of the Beer-Lambert law.
By using Beers law we will calculate the concentration of the sample. This is just saying that the output intensity will be the same or lower compared with the input intensityThis coefficient in the exponential function µ pronounced mu is dependent on the material and the energy of the x-rays. It is used in analytical chemistry to measure the absorbance of several samples.
The BeerLambert law also known as Beers law the LambertBeer law or the BeerLambertBouguer law relates the attenuation of light to the properties of the material through which the light is travelling. Geek Box 78 and every observation on the detector is Poisson distributed in the monochromatic case. The calibration curve is obtained by fitting an appropriate equation to a set of experimental data calibration data consisting of the measured responses to known concentrations of analyte.
The standard equation for absorbance is A ɛ x l x c where A is the amount of light absorbed by the sample for a given wavelength ɛ is the molar absorptivity l is the distance that the light travels through the solution and c is the concentration of the absorbing species per unit volume. A sample having a maximum absorbance value of 275nm. It refers to a device which helps specific solutions to absorb a particular wavelength of light.
303 Where log I 0 A Absorbance I K Molar extinction E 2. Formulated by German mathematician and chemist August Beer in 1852 it states that the absorptive capacity of a dissolved substance is directly proportional to its concentration in a solution. A a b c where A is the measured absorbance a is a wavelength-dependent absorptivity coefficient b is the path length and c is the analyte concentration.
A ε b c Where ε is the wavelength-dependent molar absorptivity coefficient with units of M-1 cm-1. Beer-Lambert Law is a combination of two laws. Mass Percent - mass solutemass solution x 100 mass units are the same unit for both solute and solution.
It is the absorbance of a substance placed in 1cm cuvette cell when the concentration is 1 molar. The multiplying term here will always be a number between 0 and 1. The Beer-Lambert law relates the attenuation of light to the properties of the material through which the light is traveling.
The general Beer-Lambert law is usually written as. Check out the derivation of Beer-Lambert law. A spectrophotometer value detected A070.
It has a molar absorptivity of 8400M-1cm-1. Now how does the Arrhenius equation work to determine the rate constant. Beer Lamberts law also called Beers Law discusses the absorbance of the light incident into a solution and the absorption coefficient of the solution.
In general Tt T A T H-T Ae-kt where Tt is the Temperature at time t T A is the Ambient temperature or temp of surroundings T H is the temperature of the hot object k is the positive constant and t is the time. Basically Pierre Bouger discovered the law in 1729 and published it in Essai DOptique Sur La Gradation De La LumièreJohann. Since the concentration path length and molar absorptivity are all directly proportional to the absorbance we can write the following equation which is known as the Beer-Lambert law often referred to as Beers Law to show this relationship.
In 1729 Pierre Bouguer discovered the law. Normality N - grams active soluteliters of solution Molality m - moles of solutemass of solvent not mass of solution. ε Molar absorption coefficient or molar absorptivity in m-1 cm-1 k x k.
As such Lambert-Beers law also has a probabilistic interpretation cf. The law is commonly applied to chemical analysis measurements and used in understanding attenuation in physical optics for photons neutrons. Let us see how to use the Beers law calculator to calculate the absorbance of light by a solution of molar concentration 433 10-5 molL-1Let the path length be 1 cm and the molar absorptivity be 8400 M-1 cm-1.
As in the case of Lamberts law equation 9 may be transformed into log I Io 𝑐 𝑥 11 The molar extinction co-efficient is dependent on the nature of the absorbing solute as well as on the wave length of the incident light used. The Beer-Lambert law is known by so many names because more than one law is involved. Mass Concentration kgm 3 or gL - mass of solutevolume of solution.
TThhee BBeeeerr LLaammbbeerrtt LLaaww 2. Finally equation 26 gives the method of calculation of combined intensity of radiation of polychromic radiation which is the usual case of exposure of real samples. This equation can be written as Aϵcl where ϵ is the proportionality constant called molar absorptivity or molar extinction coefficient.
Molarity M - moles of soluteliters of solution not solvent. 1cm is the width of a cuvette. The Beer-Lambert law or Beers law is the linear relationship between absorbance and concentration of an absorbing species.
The Beer Lambert Law When a monochromatic light of initial intensity Io passes through a solution in a transparent vessel some of the light is absorbed so that the intensity of the transmitted light I is less than Io There is some loss of light intensity from scattering by particles in the solution and. Other Names for Beers Law. It is assumed that a constant rate of cooling which is equal to the rate of cooling related to the.
The expression equation 11 is commonly known as Beer-Lamberts law. MathrmA varepsilon bc nonumber. This page takes a brief look at the Beer-Lambert Law and explains the use of the terms absorbance and molar absorptivity relating to UV-visible absorption spectrometry.
Beer-Lambert Law demonstrates the linear relationship between the absorbance of light and the concentration of a substance. Methods to Apply Newtons Law of Cooling. Calculate the concentration of the sample.

Beer S Law Equation And Example
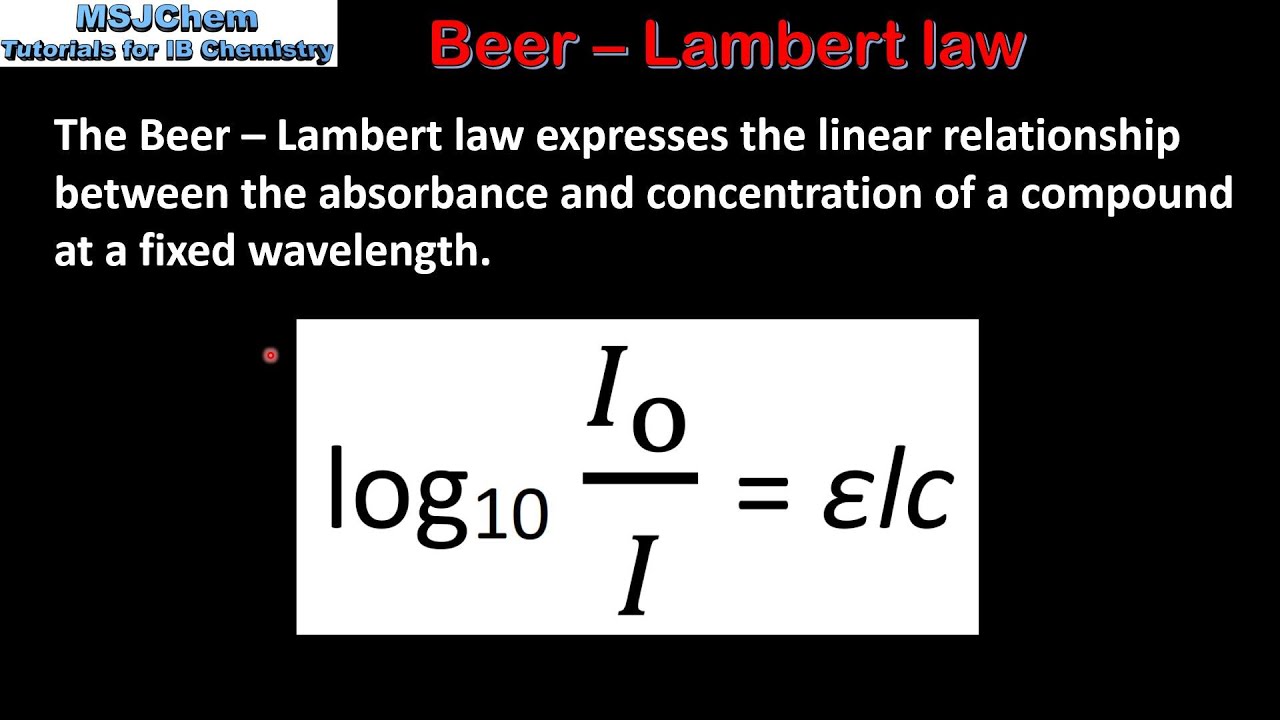
B 7 The Beer Lambert Law Hl Youtube

How To Find Molar Absorptivity Using The Beer Lambert Law Chemistry Study Com
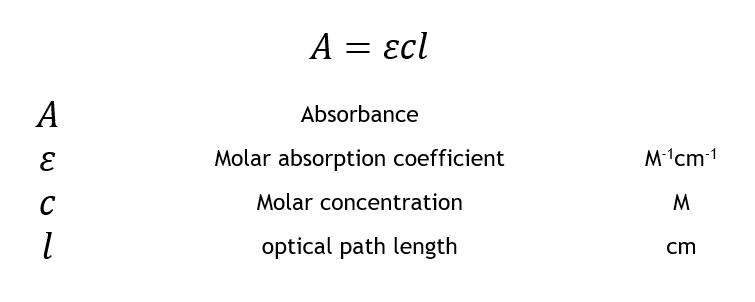
Beer Lambert Law Transmittance Absorbance Edinburgh Instruments
No comments for "Beer's Lambert Law Equation"
Post a Comment